Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ariyoshi, Gen; Saruta, Koichi; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Maeno, Koki*; Li, Y.*; Tsutsui, Kihei*
Proceedings of 20th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-20) (Internet), p.1407 - 1420, 2023/08
Cavitation damage on a target vessel due to proton beam-induced pressure waves is one of the crucial issues for the pulsed neutron source using a mercury spallation target. As a mitigation technique for the damage, the helium microbubble injection into the mercury has been carried out by using a swirl bubbler in order to utilize compressibility of bubbles. Moreover, double-walled structure, which consists of an outer wall and an inner wall, has been applied as the target head structure. In this study, we aim to develop an abnormality diagnostic technology to detect the inner wall cracking, which is caused by such cavitation damage, from the outside of the target vessel. The mercury flow fields in the case with the cracking are evaluated by computational fluid dynamics analysis based on finite element method. And then, effect of the cracking on the flow field is discussed from the point of view of the flow-induced vibration and the acoustic vibration.
 probed by anisotropic low-energy excitations
probed by anisotropic low-energy excitationsIshihara, Kota*; Roppongi, Masaki*; Kobayashi, Masayuki*; Imamura, Kumpei*; Mizukami, Yuta*; Sakai, Hironori; Opletal, P.; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Haga, Yoshinori; Hashimoto, Kenichiro*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 14, p.2966_1 - 2966_7, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:92.42(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The superconducting symmetry of the heavy fermion uranium-based superconductor UTe is investigated using low temperature penetration depth measurements. The anisotropic low-energy quasiparticle excitations indicates multiple superconducting components in a chiral complex form. The most consistent is a chiral non-unitary state.
is investigated using low temperature penetration depth measurements. The anisotropic low-energy quasiparticle excitations indicates multiple superconducting components in a chiral complex form. The most consistent is a chiral non-unitary state.

Ishihara, Kota*; Kobayashi, Masayuki*; Imamura, Kumpei*; Konczykowski, M.*; Sakai, Hironori; Opletal, P.; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Haga, Yoshinori; Hashimoto, Kenichiro*; Shibauchi, Takasada*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 5(2), p.L022002_1 - L022002_6, 2023/04
Lower superconducting critical fields 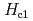 of UTe
of UTe have been determined. Orthorhombic UTe
have been determined. Orthorhombic UTe has magnetic easy axis along the
has magnetic easy axis along the  -axis. We found
-axis. We found 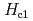 perpendicular to
perpendicular to  showed anomalous enhancement. By comparing with anisotropy of upper critical fields, effect of magnetic fluctuations on superconductivity is suggested.
showed anomalous enhancement. By comparing with anisotropy of upper critical fields, effect of magnetic fluctuations on superconductivity is suggested.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2022-063, 86 Pages, 2023/02
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "The study of oxidative stress status in the organs exposed to low dose/low dose-rate radiation" conducted from FY2019 to FY2021. Since the final year of this proposal was FY2021, the results for three fiscal years were summarized. The present study aims to investigate the biological effects of low dose/low dose-rate radiation exposure, which is of great social interest, on the oxidative stress status of individual organs and will contribute to the collection of scientific data in a dose range to be required. The samples to be analyzed in this study were collected from wild Japanese macaques exposed in the ex-evacuation zone after the accident of 1F.
Yakushev, A.*; Lens, L.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; J
llmann, Ch. E.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; J ger, E.*; Krier, J.*; Runke, J.*; Albers, H. M.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; et al.
ger, E.*; Krier, J.*; Runke, J.*; Albers, H. M.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; et al.
Frontiers in Chemistry (Internet), 10, p.976635_1 - 976635_11, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:79.28(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Flerovium (Fl, element 114) is the heaviest element chemically studied so far. The first chemical experiment on Fl suggested that Fl is a noble-gas-like element, while the second studies suggested that Fl has a volatile-metal-like character. To obtain more reliable conclusion, we performed further experimental studies on Fl adsorption behavior on Si oxide and gold surfaces. The present results suggest that Fl is highly volatile and less reactive than the volatile metal, Hg, but has higher reactivity than the noble gas, Rn.

Aoki, Dai*; Sakai, Hironori; Opletal, P.; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Ishizuka, Jun*; Yanase, Yoichi*; Harima, Hisatomo*; Nakamura, Ai*; Li, D.*; Homma, Yoshiya*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(8), p.083704_1 - 083704_5, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:96.09(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2021-050, 82 Pages, 2022/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "The study of oxidative stress status in the organs exposed to low dose/low dose-rate radiation" conducted in FY2020. The present study aims to investigate the biological effects of low dose/low dose-rate radiation exposure, which is of great social interest, on the oxidative stress status of individual organs and will contribute to the collection of scientific data in a dose range to be required. An interdisciplinary collaborative study discussed the correlation between radiation dose and the biological effect by analyzing the samples of wild Japanese macaques exposed to radiation due to the accident of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station and of animal experiments.
Nugraha, E. D.*; Hosoda, Masahiro*; Kusdiana*; Untara*; Mellawati, J.*; Nurokhim*; Tamakuma, Yuki*; Ikram, A.*; Syaifudin, M.*; Yamada, Ryohei; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11(1), p.14578_1 - 14578_16, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:84.25(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Mamuju is one of the regions in Indonesia which retains natural conditions but has relatively high exposure to natural radiation. The goals of the present study were to characterize exposure of the entire Mamuju region as a high natural background radiation area (HNBRA) and to assess the existing exposure as a means for radiation protection of the public and the environment. A cross-sectional study method was used with cluster sampling areas by measuring all parameters that contribute to external and internal radiation exposures. It was determined that Mamuju was a unique HNBRA with the annual effective dose between 17 and 115 mSv, with an average of 32 mSv. The lifetime cumulative dose calculation suggested that Mamuju residents could receive as much as 2.2 Sv on average which is much higher than the average dose of atomic bomb survivors for which risks of cancer and non-cancer diseases are demonstrated. The study results are new scientific data allowing better understanding of health effects related to chronic low-dose-rate radiation exposure and they can be used as the main input in a future epidemiology study.
Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator
JAEA-Review 2020-074, 105 Pages, 2021/03
The Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator is in charge of the operation, utilization and technical development of JRR-3 (Japan Research Reactor No.3), JRR-4 (Japan Research Reactor No.4), NSRR (Nuclear Safety Research Reactor), Tandem Accelerator, RI Production Facility and TPL (Tritium Process Laboratory). This annual report describes the activities of our department in fiscal year of 2018. We carried out the operation and maintenance, utilization, upgrading of utilization techniques, safety administration and international cooperation. Also contained are lists of publications, meetings, granted permissions on laws and regulations concerning atomic energy, outcomes in service and technical developments and so on.
Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator
JAEA-Review 2020-073, 113 Pages, 2021/03
The Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator is in charge of the operation, utilization and technical development of JRR-3 (Japan Research Reactor No.3), JRR-4 (Japan Research Reactor No.4), NSRR (Nuclear Safety Research Reactor), Tandem Accelerator, RI Production Facility and Tritium Process Laboratory. This annual report describes the activities of our department in fiscal year of 2017. We carried out the operation and maintenance, utilization, upgrading of utilization techniques, safety administration and international cooperation. Also contained are lists of publications, meetings, granted permissions on laws and regulations concerning atomic energy, outcomes in service and technical developments and so on.
Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator
JAEA-Review 2020-072, 102 Pages, 2021/03
The Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator is in charge of the operation, utilization and technical development of JRR-3 (Japan Research Reactor No.3), JRR-4 (Japan Research Reactor No.4), NSRR (Nuclear Safety Research Reactor), Tandem Accelerator, RI Production Facility and Tritium Process Laboratory). This annual report describes the activities of our department in fiscal year of 2016. We carried out the operation and maintenance, utilization, upgrading of utilization techniques, safety administration and international cooperation. Also contained are lists of publications, meetings, granted permissions on laws and regulations concerning atomic energy, outcomes in service and technical developments and so on.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2020-048, 49 Pages, 2021/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2019. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "The study of oxidative stress status in the organs exposed to low dose/low dose-rate radiation". This study investigates the biological effects of low dose/low dose-rate radiation exposure, which is of great social interest, on the oxidative stress status of individual organs and will contribute to the collection of scientific data in a dose range to be required. An interdisciplinary collaborative study discussed the correlation between radiation dose and the biological effect by analyzing the samples of wild Japanese macaques exposed to radiation due to the accident of Fukushima nuclear power station and of animal experiments.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Kyushu University*
JAEA-Review 2020-036, 176 Pages, 2021/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2019. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Research and Development of Transparent Materials for Radiation Shield Using Nanoparticles" conducted in FY2019. The present study aims to reduce radiation exposure of workers in debris retrieval/analysis and reduce deterioration of optical and electronic systems in remote cameras. For these purposes, we develop transparent radiation shield by making the shield materials into nanoparticles, and dispersing/solidifying them in epoxy resin. By making boride or heavy metal compounds into nanoparticles, we will also develop a radiation shield that shields both neutrons and gamma-rays, and also suppresses secondary gamma-rays produced from neutrons.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; University of Tsukuba*
JAEA-Review 2020-037, 53 Pages, 2020/12
JAEA/CLADS had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project in FY2019. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Upgrading of Recovery Method for Radioactive Microparticles by Heavy Liquid Separation Aiming to Volume Reduction of Contaminated Soil" conducted in FY2019.
Taya, Hidetoshi*; Park, A.*; Cho, S.*; Gubler, P.; Hattori, Koichi*; Hong, J.*; Huang, X.-G.*; Lee, S. H.*; Monnai, Akihiko*; Onishi, Akira*; et al.
Physical Review C, 102(2), p.021901_1 - 021901_6, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:69.78(Physics, Nuclear)Aritomo, Yoshihiro*; Amano, Shota*; Okubayashi, Mizuki*; Yanagi, Baku*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Ota, Masahisa*
Physics of Atomic Nuclei, 83(4), p.545 - 549, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Nuclear)Takiya, Hiroaki; Kadowaki, Haruhiko; Matsushima, Akira; Matsuo, Hidehiko; Ishiyama, Masahiro; Aratani, Kenta; Tezuka, Masashi
JAEA-Technology 2020-001, 76 Pages, 2020/05
Advanced Thermal Reactor (ATR) FUGEN was operated for about 25 years, and now has been proceeding decommissioning after the approval of the decommissioning plan in Feb. 2008. The reactor, heavy water system and helium system are contaminated by tritium because of neutron absorption of heavy water, which is a moderator. Before dismantling these facilities, it is necessary to remove tritium from them for not only reducing the amount of tritium released to surrounding environment and the risk of internal exposure by tritium but also ensuring the workability. In first phase of decommissioning (Heavy Water and Other system Decontamination Period), tritium decontamination of the reactor, heavy water system and helium system started in 2008 and completed in 2018. This report shows the results of tritium decontamination of the reactor, heavy water system and helium system.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Kyushu University*
JAEA-Review 2019-039, 104 Pages, 2020/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Center of World Intelligence Project for Nuclear Science/Technology and Human Resource Development (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2018. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Research and Development of Transparent Materials for Radiation Shield using Nanoparticles". The present study aims to reduce radiation exposure of workers in debris retrieval/analysis and reduce deterioration of optical and electronic systems in remote cameras. For these purposes, we develop transparent radiation shield by making the shield materials into nanoparticles, and dispersing/solidifying them in epoxy resin. By making B C and W into nanoparticles, we will also develop a radiation shield that shields both neutrons and gamma-rays, and also suppresses secondary gamma-rays produced from neutrons.
C and W into nanoparticles, we will also develop a radiation shield that shields both neutrons and gamma-rays, and also suppresses secondary gamma-rays produced from neutrons.
 Si
Si without local inversion symmetry
without local inversion symmetryNakamura, Shota*; Hyodo, Kazushi*; Matsumoto, Yuji*; Haga, Yoshinori; Sato, Hitoshi*; Ueda, Shigenori*; Mimura, Kojiro*; Saiki, Katsuyoshi*; Iso, Kosei*; Yamashita, Minoru*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 89(2), p.024705_1 - 024705_5, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:22.16(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; University of Tsukuba*
JAEA-Review 2019-023, 33 Pages, 2020/01
CLADS, JAEA, had been conducting the Center of World Intelligence Project for Nuclear Science/Technology and Human Resource Development (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2018. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the 'Upgrading of Recovery Method for Radioactive Microparticles by Heavy Liquid Separation Aiming to Volume Reduction of Contaminated Soil'. After the accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, radioactive cesium has been heterogeneously distributed in surface soil due to the existence of radioactive microparticles and clay minerals. Therefore, the selective removal of these microparticles will lead to the volume reduction of contaminated soil. The present study examines methods for selectively removing radioactive microparticles from soil. Also, in order to reduce the volume of contaminated soil, we search a possibility to practically apply the separation method that uses the difference in specific gravity of particles (heavy liquid separation method).